What does your body do to stop the bleeding?
Overview
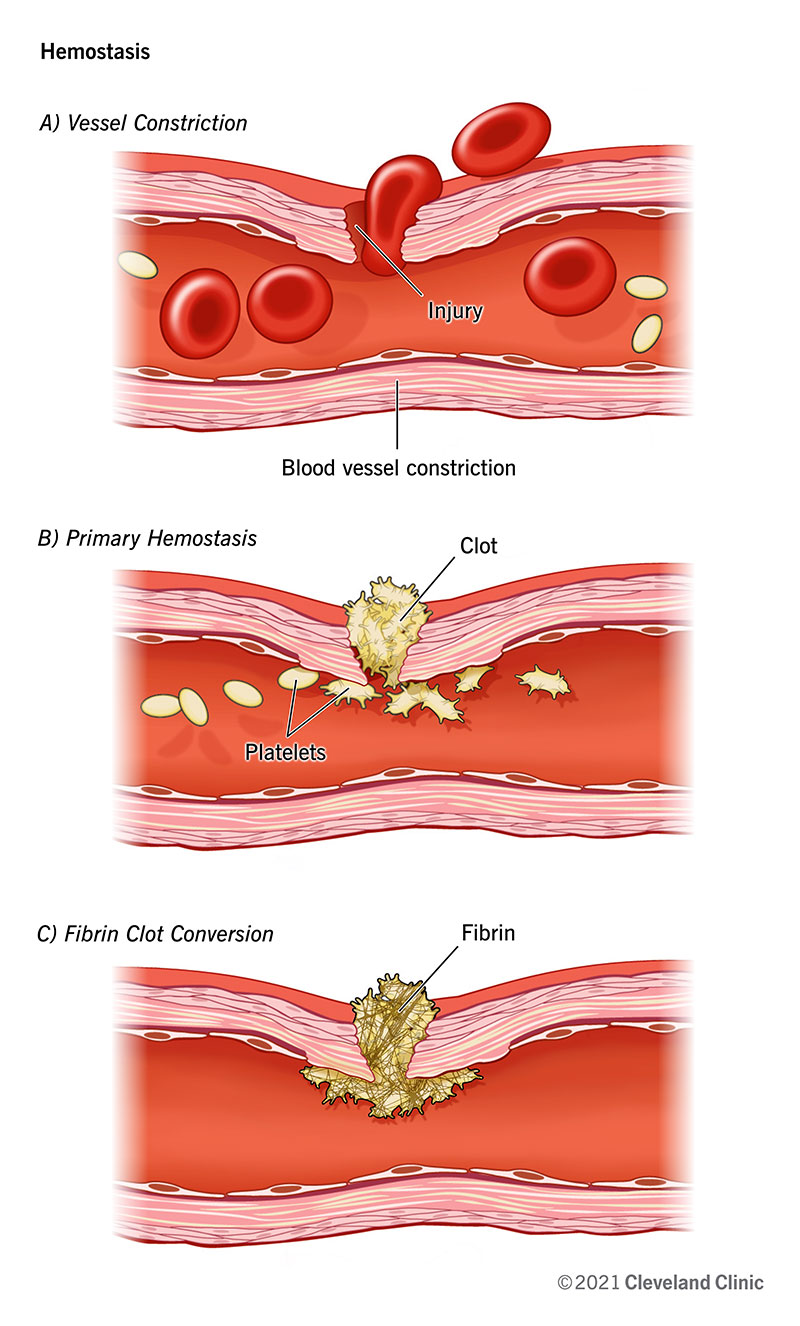
What is hemostasis?
Hemostasis is your trunk's normal reaction to an injury that causes bleeding. This reaction stops bleeding and allows your body to starting time repairs on the injury. This capability is essential to continue you alive, particularly with significant injuries. However, in uncommon cases, the processes that command hemostasis can malfunction, causing potentially serious — or even dangerous — bug with haemorrhage or clotting.
How does hemostasis work?
Hemostasis combines the terms "hemo" (significant "blood") and "stasis" (meaning "continuing yet"). In this context, it'south the term for how your torso stops bleeding. Rather than existence just a unmarried process, hemostasis is really a drove of several processes. Though they look like separate processes, these all happen at the same fourth dimension when your body forms a blood clot.
Primary hemostasis (platelet clotting)
Primary hemostasis is when your body forms a temporary plug to seal an injury. To accomplish that, platelets that circulate in your blood stick to the damaged tissue and actuate. That activation ways they tin can "recruit" more platelets to form a platelet "plug" to terminate blood loss from the damaged area. That jell works much like a cork or canteen stopper, keeping blood in and debris or germs out. Primary hemostasis may also involve constriction (narrowing) of the damaged blood vessel, which tin can happen because of substances that activated platelets release.
Secondary hemostasis (coagulation cascade)
The platelet plug is the first pace to stop bleeding, merely it isn't stable enough to stay in identify without help. The next step, which stabilizes the plug, is secondary hemostasis. This step, sometimes called coagulation, involves molecules in your blood chosen "coagulation factors." Those factors activate in sequence, the "coagulation cascade," which amplifies clotting effects as the sequence continues. Ultimately, the coagulation cascade forms a substance chosen fibrin. During this footstep, the platelet plug acts similar bricks and the fibrin acts like mortar. Together, they form a solid, stable clot.
Fibrin clot remodeling
The last stage of hemostasis is when your body remodels the existing clot into a fibrin clot. Your trunk does that because blood clots are a temporary patch, non a permanent solution. That removal involves a process called fibrinolysis. During fibrinolysis, your trunk remodels the clot into the same kind of tissue that was at that place before the injury.
Possible Causes
What causes hemostasis?
Your body naturally monitors itself for injuries, and when it detects one, it reacts quickly to take control of the situation. Without normal hemostasis, even minor injuries could cause unsafe claret loss. An example of this is hemophilia, a condition where hemostasis doesn't work properly and blood can't clot effectively. Whatsoever suspension in your skin is as well a risk for germs to enter your torso. Clots assistance reduce that take a chance past sealing the injury.
What potential health problems tin can happen with hemostasis?
Hemostasis refers to normal blood clotting in response to an injury. However, your body can besides take too much clotting, known as hypercoagulability. That tin cause many blood clots to class spontaneously and cake normal blood menses. When blood clots form inside your blood vessels, this is known as thrombosis. When you have thrombosis that happens repeatedly, that's a condition called thrombophilia.
Thrombophilia (hypercoagulability or too much clotting)
Hypercoagulability is when your blood clots also much or likewise easily. This is unsafe because those clots tin can develop or go stuck in different places in your body and cause severe, life-threatening problems. Examples of these problems include:
- Stroke.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which can and then cause a pulmonary embolism.
- Middle attack.
Many types of cancer tin can cause hypercoagulability, and some rare weather that cause hypercoagulability are also genetic. That ways they are either inherited from your parents or happen because of a random mutation in your DNA. People with these conditions take thrombophilia. A few examples of conditions like this include:
- Protein C deficiency.
- Prothrombin factor mutation.
- Gene 5 Leiden mutation.
Inherited disorders that cause thrombophilia aren't as common as "caused" atmospheric condition, which you commonly develop later in life. Examples of caused conditions include:
- Antiphospholipid syndrome.
- Inflammatory bowel disease.
- Severe reactions to infections, such every bit sepsis.
Most medications that treat thrombophilia make it harder for your claret to clot in some way. Examples of these include antiplatelet, anticoagulant and fibrinolytic (fibrin-breaking or jell-busting) drugs.
Hypocoagulability (not plenty clotting)
When your blood doesn't jell well, any injury becomes a much more dangerous consequence. Without proper clotting, even pocket-size injuries can crusade you to lose a lot of blood. Information technology likewise means yous're at greater risk for injuries to organs and claret vessels within your body, which tin can and so cause internal bleeding.
Certain types of cancer like leukemia can crusade you to bleed likewise easily. That'due south because they oftentimes involve a lack of platelets in your body or anti-clotting action. Conditions that keep your blood from clotting are often genetic, also. Some examples of genetic conditions include:
- Hemophilia.
- Von Willebrand disease.
- Inherited thrombocytopenia (low platelet count).
Treating atmospheric condition that continue your blood from clotting normally involves medications that slow down or block your body's anti-clotting processes, that boost your body'due south power to brand platelets or that add more than of certain clotting factors to your blood. You can also receive transfusions of platelets to add together more if your torso needs them.
How are hemostasis issues diagnosed?
A healthcare provider — such as a hematologist — can diagnose blood clotting problems based on your symptoms and blood tests that analyze the clotting-related components in a sample of your blood.
When to Call the Doctor
When should I telephone call a doctor well-nigh problems with clotting?
Hypercoagulability can happen with a variety of dissimilar symptoms depending on where and when an abnormal jell develops. Examples of this include:
- Brain: Stroke symptoms, including weakness or paralysis on one or both sides of your body, slurring oral communication, disability to move one side of your face and headache.
- Middle: Heart attack symptoms, including breast hurting, shortness of breath, weakness, fast or irregular heartbeat, centre palpitations (feeling your own heartbeat) and passing out.
- Lungs: Pulmonary embolism symptoms, including wheezing or sudden problems animate, pain in your chest, coughing blood, fingertips or lips that are stake or blue-tinted and passing out.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): This tin often pb to pulmonary embolism. Symptoms include pain in the calf or elsewhere in the leg, as well as swelling or redness. However, blood clots in your leg can sometimes have relatively minor symptoms, and may just feel similar a pulled muscle.
- Kidneys: Blockages in your kidney tin crusade blood in your urine (pee), needing to pee less frequently and hurting in your lower back on either side of your spine.
Hypocoagulability will cause y'all to bleed more easily. Most oftentimes, this causes the following symptoms:
- Nosebleeds that are hard to cease.
- Bleeding effectually your gums when you lot brush your teeth.
- Wounds that may seep or ooze blood for a long time and take much longer to heal. However cuts in certain areas, such as the face, fingertips or scalp, can accept a long fourth dimension to stop bleeding considering there are many more claret vessels in those areas than in other places in your body.
- Finding bruises and you can't remember how you got them or bruising much more than hands and visibly (bruises are bigger and more than colorful).
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Hemostasis is a natural part of your daily life. It helps your body protect itself from haemorrhage and infection, and recover from injuries large and small. Understanding how information technology works tin can help you improve intendance for yourself. It also means you can recognize potential issues with your body's natural recovery abilities and go assist sooner rather than later.
mcknightsucan1991.blogspot.com
Source: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/21999-hemostasis
0 Response to "What does your body do to stop the bleeding?"
Publicar un comentario